The shocking reality of indoor heat deaths in Arizona exposes a growing crisis that challenges both infrastructure and policy.
Story Highlights
- Indoor heat deaths in Arizona are rising, highlighting infrastructure and policy failures.
- The situation underscores the need for immediate policy action to protect vulnerable citizens.
- Authorities face criticism for inadequate responses to extreme heat conditions.
- Community efforts are rising to address the gap.
Rising Indoor Heat Deaths in Arizona
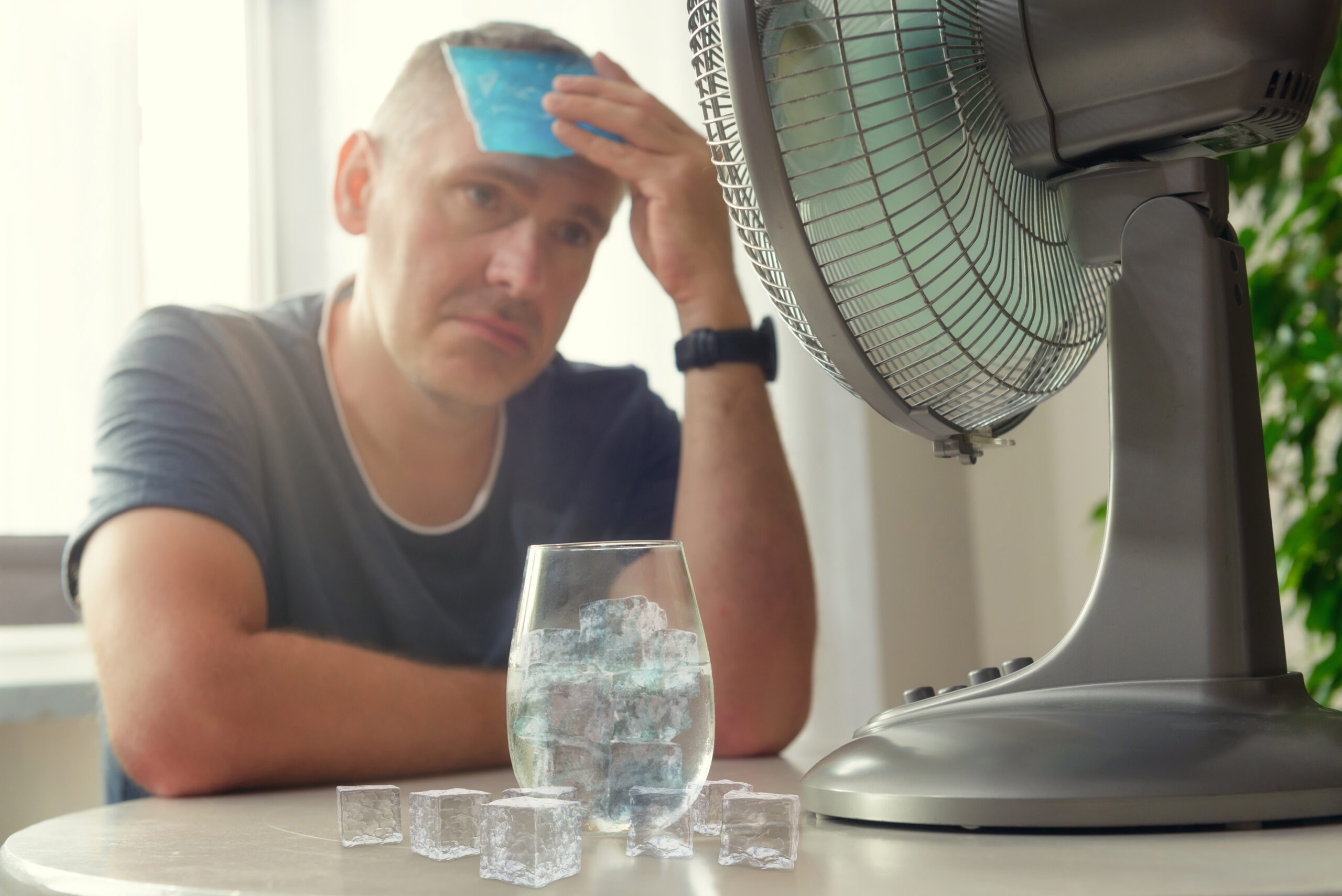
Arizona faces a dramatic increase in indoor heat-related deaths, primarily affecting the most vulnerable populations. Record-breaking temperatures, exacerbated by climate change, have pushed indoor environments to dangerous levels, leading to fatalities among those unable to afford cooling solutions. This crisis highlights the urgent need for policy reforms and infrastructure improvements to prevent further tragedies and protect citizens from extreme heat conditions.
Arizona’s government response has been criticized for not adequately addressing the root causes of indoor heat deaths. Moreover, the lack of enforcement of building standards that could mitigate indoor heat is seen as a significant oversight. As temperatures continue to rise, the pressure mounts on policymakers to implement more robust solutions.
The Arizona Heatwave death toll has now hit over 400 lives and it’s coming for your State! Imagine trying to live without AC even for a few hours when a lot of people don’t have any at all.Imagine the Immigrants that are out in this weather from sun up to sun down daily! Imagine pic.twitter.com/MWDHu2L6ev
— Suzie rizzio (@Suzierizzo1) August 16, 2025
Community Efforts and Advocacy
In response to government inaction, local communities and advocacy groups have stepped up to provide relief. Initiatives include distributing cooling devices, setting up emergency cooling centers, and raising awareness about the dangers of indoor heat. These grassroots efforts highlight a community-driven approach to a problem that requires immediate attention. The involvement of non-profit organizations and volunteers has been crucial in bridging the gap left by governmental measures.
Despite these efforts, the underlying infrastructure issues remain unaddressed. Long-term solutions may require significant investment in energy-efficient building designs and sustainable cooling technologies. Without such measures, indoor heat deaths may continue to rise, presenting a persistent threat to public health and safety.
Watch:
Future Policy Directions
Policymakers are urged to prioritize the adoption of comprehensive strategies that address both the symptoms and causes of indoor heat deaths. This includes revising building codes, increasing funding for energy assistance programs, and enhancing public education on heat safety. Furthermore, collaboration with technology and energy sectors could foster innovations that make cooling solutions more accessible and affordable.
As Arizona grapples with the realities of a warming climate, it serves as a stark reminder of the broader implications of climate change on human health. The state’s experience could inform national policies aimed at safeguarding vulnerable populations from extreme weather conditions. The coming years will test the resilience of both governmental frameworks and community networks in adapting to these environmental challenges.
Sources:
RESAS D5.3 Stakeholder Analysis Final
What is Stakeholder Analysis?
Stakeholder Analysis
Skills in Stakeholder Analysis
Guide to Stakeholder Analysis